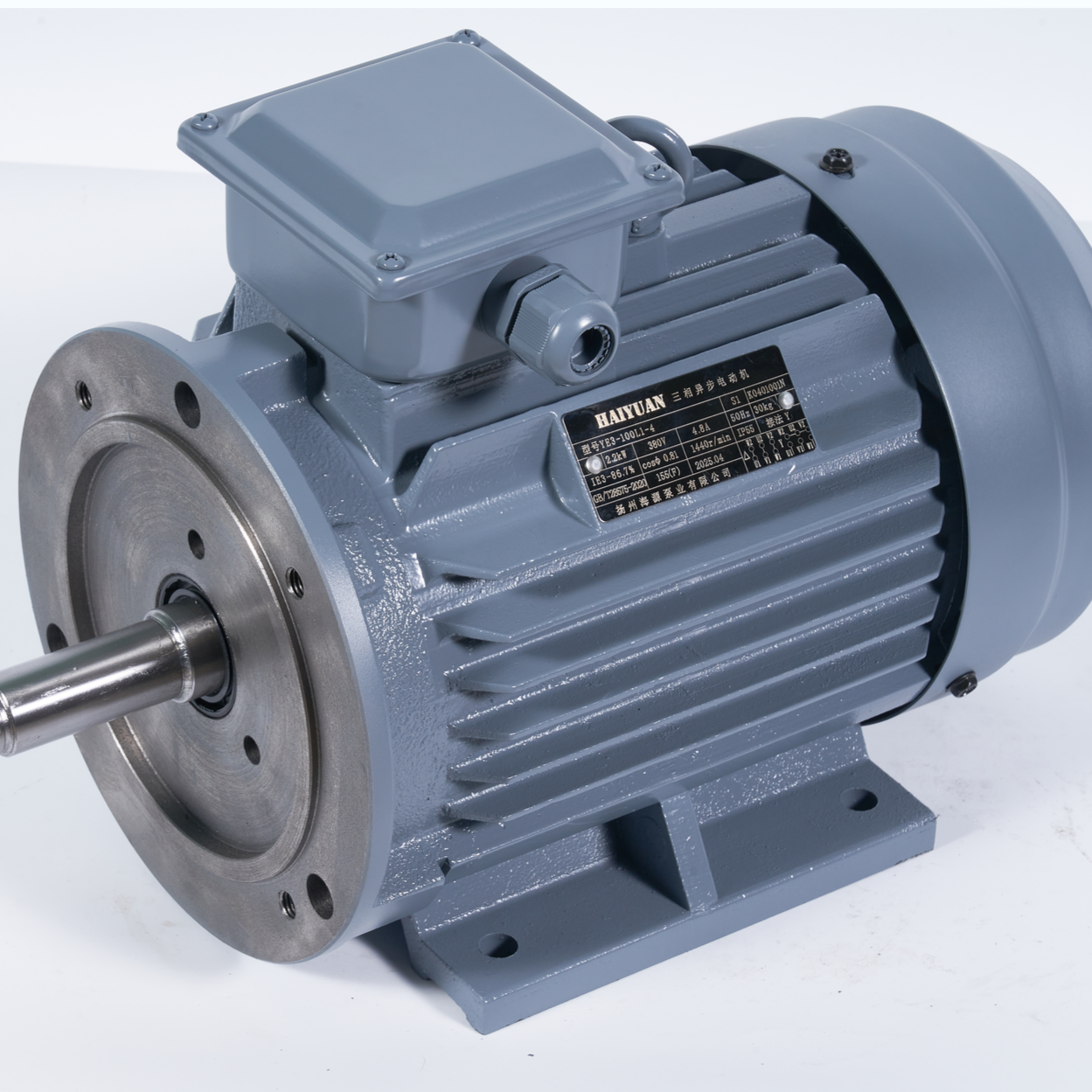
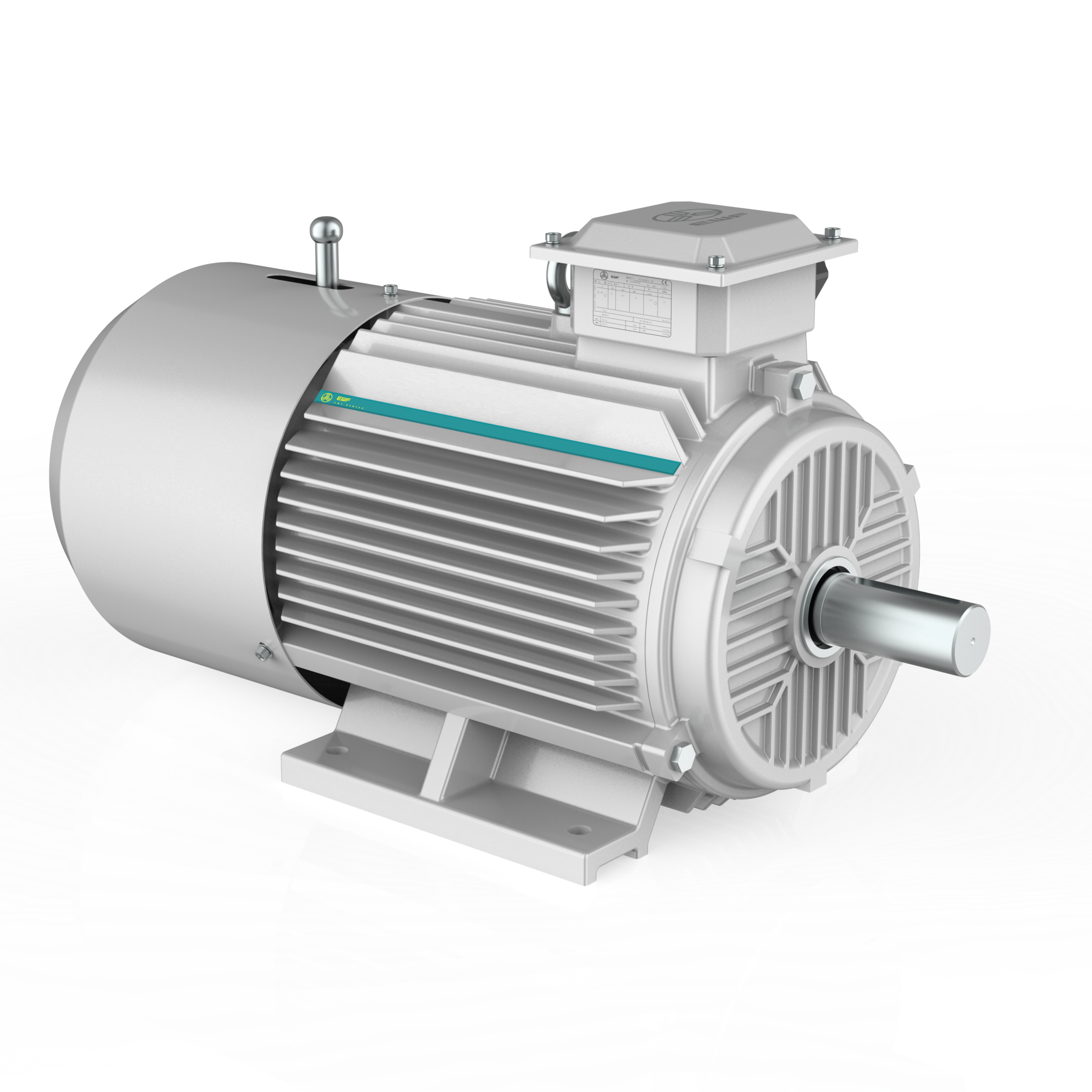
asynchronous electric motor
The asynchronous electric motor, also known as an induction motor, stands as a cornerstone of industrial power generation. This robust electrical machine operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the rotating magnetic field in the stator induces current in the rotor conductors. The motor's distinguishing feature lies in its operational speed, which remains slightly lower than the synchronous speed, creating the characteristic slip that gives it its asynchronous nature. The motor consists of two main components: a stationary stator containing windings connected to the power source and a rotating rotor with embedded conductors. When three-phase AC power energizes the stator windings, it generates a rotating magnetic field that induces currents in the rotor, producing electromagnetic torque and initiating rotation. Modern asynchronous motors incorporate advanced features such as variable frequency drives for speed control, enhanced cooling systems, and high-efficiency designs. These motors find widespread applications across various industries, from powering industrial machinery and conveyor systems to driving pumps, fans, and compressors. Their reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness make them the preferred choice for most industrial applications, accounting for approximately 80% of industrial motor usage worldwide.