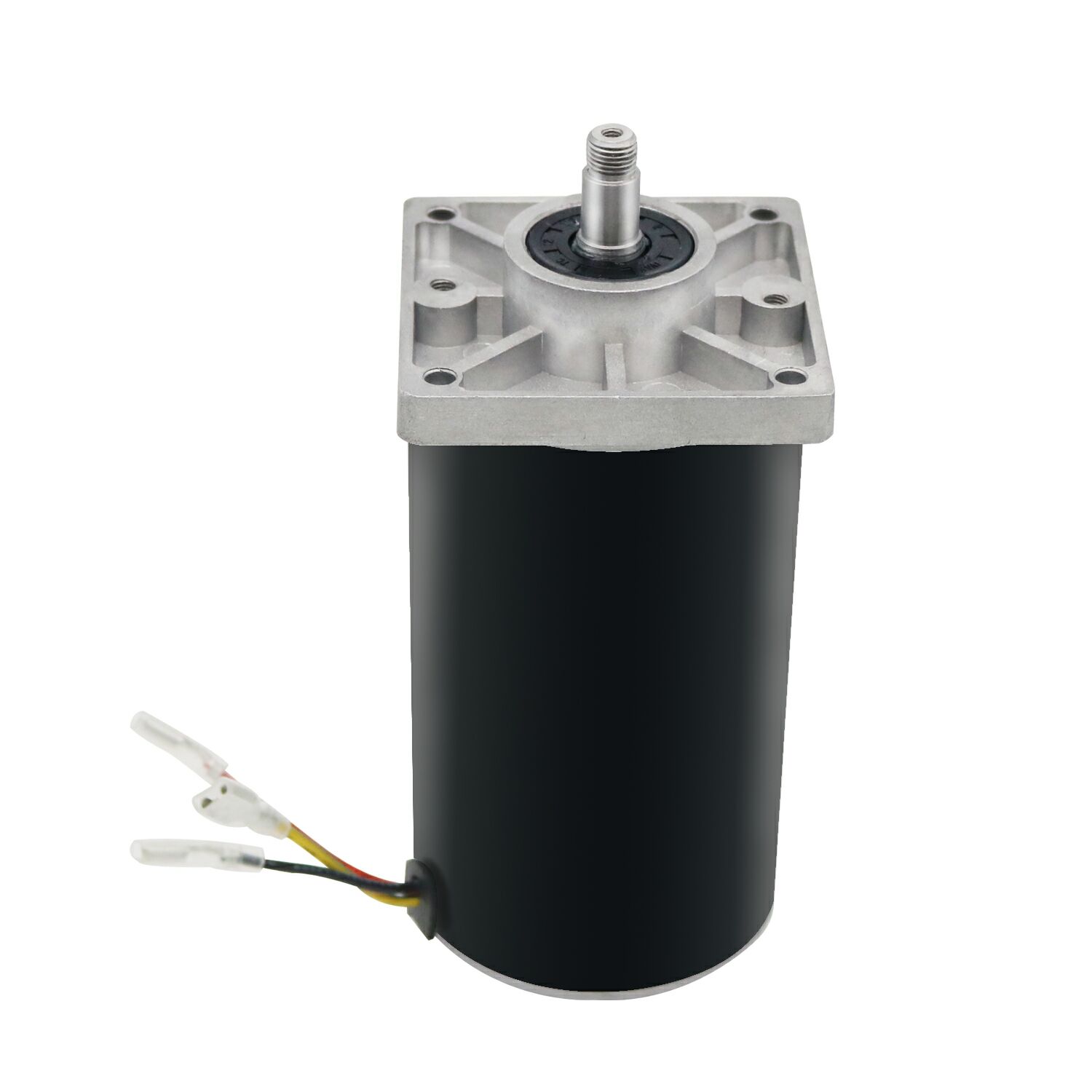
רוטור קג
רוטור סנדויצ'י הוא רכיב קריטי במנועים חשמליים, במיוחד במנועים אינדוקטיביים, והוא ייחודי בשל בנייתו הכוללת מוטות מוליכים הטומנים בלב גלילי. העיצוב הבסיסי כולל מוטות אלומיניום או נחושת המסודרים במבנה גלילי, המחוברים משני הקצוות במעגלים מוליכים, וсоздים מבנה הדומה לובן של סנאי. הרוטור פועל על פי עקרונות האינדוקציה האלקטרומגנטית, כאשר שדה המגנטי הסובב שמגיעה מהסטטור מעורר זרמים במוטות הסנדויץ', וсозд שדה מגנטי שניוני. האינטראקציה הזו יוצרת את המומנט הדרוש להפעלת המנוע. עיצוב הרוטור הסנדויצ'י מצטיין באיכותו ובניכיונו, מה שעושה אותו לאידיאלי ליישומים תעשייתיים מגוונים. הבנייה שלו מאפשרת פיזור חום יעיל, דרישות מזעריות לתפעול שוטף, ותפקוד עקבי בתנאי הפעלה שונים. העיצוב הפשוט אך היעיל של הרוטור מאפשר לו לעמוד ב момנט הפעלה גבוה ולפעול ביעילות בسرסורים שונים. טכניקות ייצור מתקדמות שיפרו עוד יותר את יכולות הרוטור הסנדויצ'י, תוך שילוב של חומרים מתקדמים והנדסה מדויקת כדי למקסם את הביצועים ואת יעילות האנרגיה. רוטורים אלו משמשים ביישומים מגוונים החל ממכשור תעשייתי ועד מערכות מיזוג, מה שמוכיח את גיוויונם ודיוקם בסביבות הפעלה מגוונות.